Knee clearance is a fundamental aspect of accessibility that plays a crucial role in accommodating individuals with disabilities, particularly those who use wheelchairs or other mobility aids. The Americans with Disabilities Act (ADA) sets specific guidelines to ensure that fixtures such as sinks, counters, and tables are designed with sufficient , allowing learn about sink height ADA here for comfortable and safe use. This article explores the significance of ADA knee clearance, the requirements established by the ADA, and best practices for implementation.
The Importance of ADA Knee Clearance
- Facilitating Independence: Adequate knee clearance empowers individuals with mobility impairments to access and use essential facilities independently. This autonomy is vital for enhancing quality of life and personal dignity.
- Promoting Safety: Proper knee clearance minimizes the risk of accidents by allowing users to navigate spaces without obstruction. This is particularly important in public areas where a diverse range of individuals may be present.
- Ensuring Legal Compliance: Meeting ADA knee clearance requirements is a legal obligation for many public and commercial facilities. Compliance not only helps avoid legal issues but also demonstrates a commitment to inclusivity.
Key ADA Knee Clearance Requirements
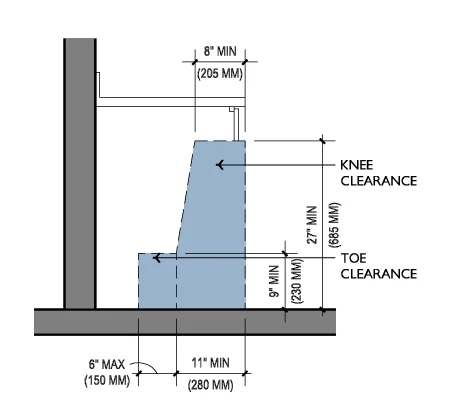
- Height Specifications: The ADA mandates that knee clearance under tables, counters, and sinks must be at least 27 inches high. This height accommodates individuals in wheelchairs, providing enough space for comfortable positioning.
- Depth and Width: The minimum depth for knee clearance should be 8 inches from the front edge of the fixture to any back wall or obstruction. The width should be at least 30 inches to allow sufficient access and maneuverability.
- Unobstructed Space: It is essential that knee clearance areas are free from obstructions, such as plumbing, structural supports, or other fixtures. This ensures that users can easily approach and utilize the space without difficulty.
- Level Surfaces: The ground beneath sinks and counters should be level. Any slopes or changes in elevation can create barriers for individuals using mobility devices.
Best Practices for Implementation
- Incorporate Universal Design Principles: Using universal design principles ensures that spaces are accessible to a broad range of users, not just those with disabilities. This approach creates environments that enhance usability for everyone.
- Stay Informed: Regularly review ADA guidelines and local building codes to ensure that all knee clearance requirements are met during the design and renovation of spaces.
- Engage Users in the Design Process: Involving individuals with disabilities in the design phase can provide valuable insights into their specific needs and preferences, leading to more effective solutions.
- Conduct Regular Inspections: Periodically check knee clearance areas to ensure they remain unobstructed and functional. This is particularly important in public facilities where the environment may change over time.
- Educate Staff and Users: Raising awareness about the importance of knee clearance and overall accessibility can foster a more inclusive environment. Training staff to assist individuals with disabilities enhances usability and support.
Conclusion
ADA knee clearance is a crucial component in creating accessible and inclusive environments. By understanding and implementing the specific requirements set forth by the ADA, designers, architects, and facility managers can ensure that all individuals can navigate spaces comfortably and independently. Prioritizing knee clearance not only meets legal obligations but also reflects a commitment to inclusivity and respect for all users. Investing in accessible design enhances the overall experience for everyone and contributes to a more equitable society.

About the author